➕ Sum or Max of Multiple Columns
Configurable Joins makes it easy to use the aggregate SQL functions like SUM() or MAX(). However, these operate across rows - what you want the max or sum of several columns on the same row? 🚣♀️
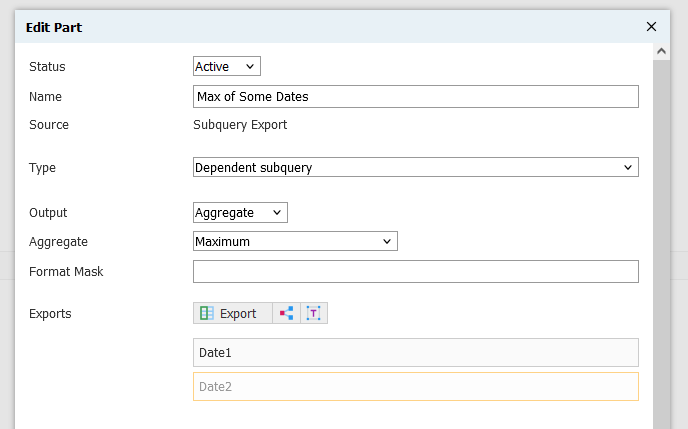
Example of trying and failing to use Maximum on multiple exports:
Solution: Table value constructors make it easy to apply aggregate functions across columns. Example use cases:
- Select the latest of three or more dates from different bases
- Select the minimum of three or more dates
- Compute the average of multiple exports
This article lists two examples, but any aggregate function will work.
Max
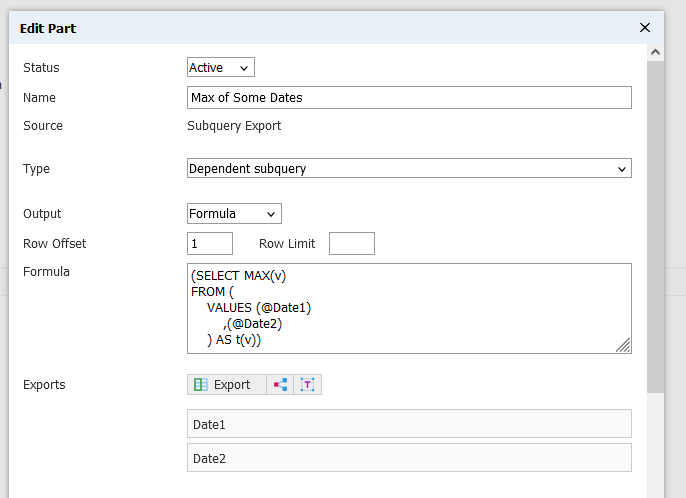
A table value constructor can also return the maximum non-null value from a set:
(SELECT MAX(v)
FROM (
VALUES (@value1)
,(@value2)
) AS t(v))However, there’s an easier way: the GREATEST() function! It does essentially the same thing with less fuss.
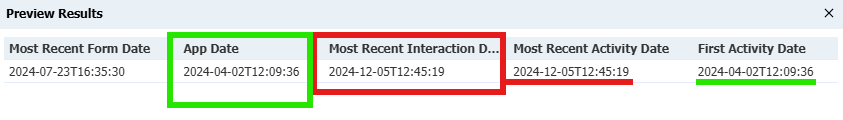
GREATEST(@value1, @value2)In practice, the GREATEST and LEAST function will allow you to compare dates from multiple different sources efficiently, such as trying to display a single "Most Recent Activity Date" that compares date values from form submissions, interactions, and application activity in one column on a report, using a subquery export:
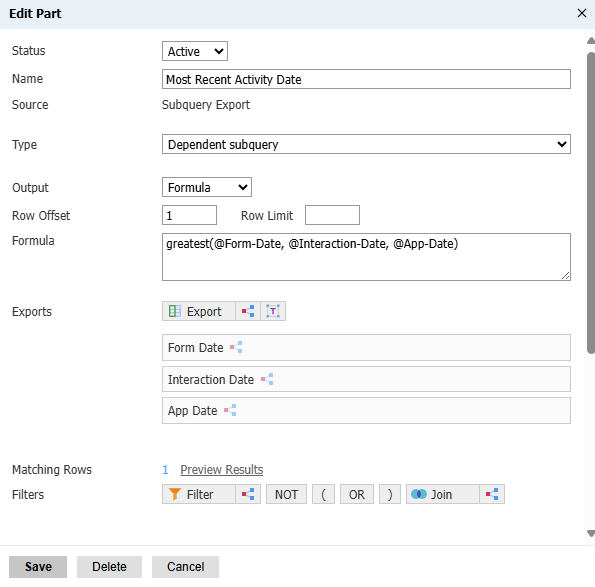
This can make certain reports more user-friendly to read.
Sum
Easily sum all non-null values from a set. Replace @valueX with your whatever exports you desire.
(SELECT SUM(v)
FROM (
VALUES (@value1)
,(@value2)
) AS t(v))Occasionally, you may encounter datatype errors when all values are NULL and have datatypes incompatible with SUM(). Adding the following extra “value” should prevent this.,(cast(NULL AS INT)) /* Prevent datatype error */

No comments to display
No comments to display